An adjective is a word which describes a noun. In the hieroglyphic language of Ancient Egypt the adjective “agrees” with the noun (i.e. an adjective for a female noun also has the female ending “t”, and adjectives for plural nouns are also plural).

bin (evil)

s bin (evil man)
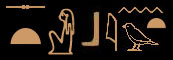
st bint (evil woman)
Word Order
Unlike English, the adjective generally follows the noun it describes (as above, “s bin” translates as “evil man” not “man evil”). However, an adjective can also be used as a “predicate adjective” (e.g. “The cat is graceful”), in which case the noun follows the adjective.
An adjective can also be used as a noun, in which case it will have a determinative sign to shows that it is a noun.
Common Adjectives
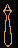
‘a (great, big)
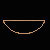
nb (every)

wr (great, mighty)

bin (bad, evil)
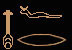
nfr (good, beautiful)

w’b (pure)
This
The word “this” also acts like an adjective and so it follows the noun and agrees with it in gender and number.
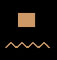
pn (this – masculine)

tn (this – feminine)
nb: “every” or “lord”
The word “nb” can act like an adjective (following and agreeing with the noun). In this case, it is translated as “all”, “every” or “any”. However, if the word “nb” appears before the noun, it has a completely different meaning, and is translated as “lord” or “master”.
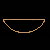
nb

ndjs nb (every individual)

nb abdju (Lord of Abydos)
Hieroglyphs Resources
- Gardiner’s sign list
- Single consonant signs
- Phonograms, Logograms and Determinatives
- Nouns and Prepositions
- Relative Forms
- Pronouns
- Word Order
- Verbs forms
- Past and Present tense
Copyright J Hill 2010